(P307) Relationship between HLA sensitization and heart transplant outcome
Location: Platinum Ballroom
Poster Presenter(s)
Aim: The immunological challenge over the past ten years was thought to be linked to the rising use of VADs as a bridging strategy, an increase in adult congenital heart surgery survivors, and a rise in the number of people in need of transplantation. As the number of patients waiting for transplant increases and there is a shortage of donor organs, even patients with a high sensitization level have to undergo transplantation. In this study, we aimed to investigate the relationship between the outcome following transplantation and the pre-transplant HLA antibody test results obtained prior to transplantation
Method: Between June 2014 and November 2023, 132 HT procedures were performed in Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital. Patients who didn’t perform cytometric crossmatch (FCXM) and those who were pediatric ( <18 years) were excluded. In total 121 HT recipients were included.
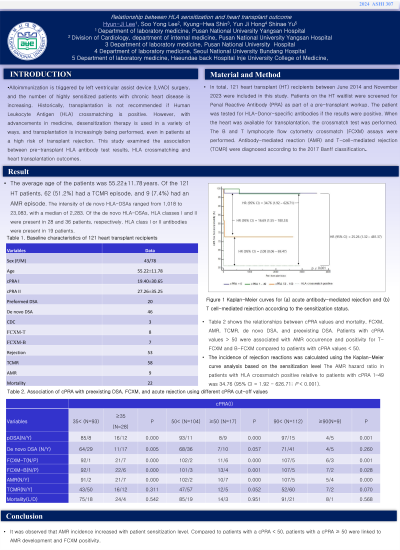
Results: The average age of the patients was 55.22. Among the 121 heart transplant patients, 62 (51.2%) had a TCMR episode, and 9 (7.4%) had an AMR episode. AMR occurrence, FCXM-T, and FCXM-B were statistically significantly correlated with preexisting DSA. In univariate analysis, AMR incidence rate was higher in cases with cPRAI >50, FCXM-B positive, FCXM-T positive, and preexisting DSA than in cases with cPRAI <50, FCXM-B negative, FCXM-T negative, and no preexisting DSA, respectively. In multivariate analysis, cPRAI 50 is associated with AMR (hazard ratio, 9.91; 95% CI 1.77-55.51, p=0.009). A Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that pre-transplant cPRA 50≥ patients had shorter AMR-free survival time (χ2 =39.21, p < 0.001). Furthermore, Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that pre-transplant FCXM-B positive patients had a shorter AMR-free survival time (χ2 = 24.34, p < 0.001).
Four categorized the level of sensitization. HLA crossmatch positive, cPRA 1-49, cPRA 50-100, and nonsensitized were the classifications given to the patients with cPRA 0. The incidence of rejection reactions was calculated using a Kaplan Meier curve analysis based on the sensitized level. The hazard ratio of AMR in patients with HLA crossmacth positive relative to patients with cPRA 1-49 was 34.76 (95% CI = 1.92 - 626.71; p < 0.001).
Conclusion: In our study, the AMR-free survival decreases with increasing sensitization.
Method: Between June 2014 and November 2023, 132 HT procedures were performed in Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital. Patients who didn’t perform cytometric crossmatch (FCXM) and those who were pediatric ( <18 years) were excluded. In total 121 HT recipients were included.
Results: The average age of the patients was 55.22. Among the 121 heart transplant patients, 62 (51.2%) had a TCMR episode, and 9 (7.4%) had an AMR episode. AMR occurrence, FCXM-T, and FCXM-B were statistically significantly correlated with preexisting DSA. In univariate analysis, AMR incidence rate was higher in cases with cPRAI >50, FCXM-B positive, FCXM-T positive, and preexisting DSA than in cases with cPRAI <50, FCXM-B negative, FCXM-T negative, and no preexisting DSA, respectively. In multivariate analysis, cPRAI 50 is associated with AMR (hazard ratio, 9.91; 95% CI 1.77-55.51, p=0.009). A Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that pre-transplant cPRA 50≥ patients had shorter AMR-free survival time (χ2 =39.21, p < 0.001). Furthermore, Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that pre-transplant FCXM-B positive patients had a shorter AMR-free survival time (χ2 = 24.34, p < 0.001).
Four categorized the level of sensitization. HLA crossmatch positive, cPRA 1-49, cPRA 50-100, and nonsensitized were the classifications given to the patients with cPRA 0. The incidence of rejection reactions was calculated using a Kaplan Meier curve analysis based on the sensitized level. The hazard ratio of AMR in patients with HLA crossmacth positive relative to patients with cPRA 1-49 was 34.76 (95% CI = 1.92 - 626.71; p < 0.001).
Conclusion: In our study, the AMR-free survival decreases with increasing sensitization.

