MISBHAVING CELLS – Deceased Donor with Crohn’s Disease Showed Complete Depletion of Circulating B Cells
(P322) Misbhaving cells – Deceased donor with Crohn’s disease showed complete depletion of circulating B cells
Location: Platinum Ballroom
Poster Presenter(s)
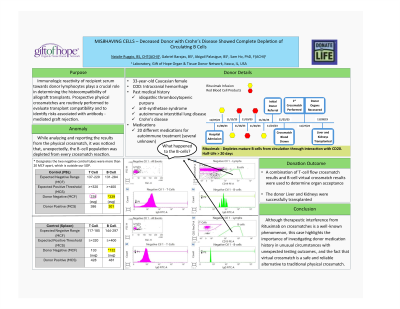
Body: Immunologic reactivity of recipient serum towards donor lymphocytes plays a crucial role in determining the histocompatibility of allograft transplants. Organ recipients with pre-existing antibodies against donor HLA may be at risk for acute antibody-mediated rejection of the graft; prospective physical crossmatches are routinely performed to evaluate transplant compatibility and to identify such risks. A 33-year-old female was referred as a potential organ donor after suffering an intracranial hemorrhage. The donor’s past medical history included idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, anti-synthetase syndrome, autoimmune interstitial lung disease and Crohn’s disease. Donor crossmatch with multiple recipient candidates was performed by the flow cytometric method using pronase-treated peripheral blood lymphocytes. While analyzing and reporting of the crossmatch results, it was noticed that, unexpectedly, the B-cell population was depleted from every crossmatch reaction. To exclude the possibility of technical errors or reagent issues, donor lymphocytes were re-stained with freshly prepared CD3/CD19 mAb and lymphocyte isolation was also re-attempted from spleen tissue, yet B cells remained undetectable. Upon more in-depth review and investigation of the donor’s medical history, it was discovered that she was receiving regular infusions of corticosteroid dexamethasone and Rituximab, an immunotherapeutic commonly used for the treatment of several forms of cancer and autoimmune diseases by depleting mature B cells from circulation through interaction with CD20. Due to the long half-life of the antibody of >20 days, drawing new blood specimens would not have allowed successful recovery of B cells for crossmatch. Organ allocation and acceptance would need to be determined via a secondary method. Using a combination of T-cell flow crossmatch and B-cell virtual crossmatch results, both kidneys and the liver were able to be allocated and successfully transplanted.
Conclusion: Although therapeutic interference from Rituximab on crossmatches is a well-known phenomenon, this case highlights the importance of investigating donor medication history in unusual circumstances with unexpected testing outcomes, and the fact that virtual crossmatch is a safe and reliable alternative to traditional physical crossmatch.
Conclusion: Although therapeutic interference from Rituximab on crossmatches is a well-known phenomenon, this case highlights the importance of investigating donor medication history in unusual circumstances with unexpected testing outcomes, and the fact that virtual crossmatch is a safe and reliable alternative to traditional physical crossmatch.

