DESENSITIZATION OF HLA ANTIBODIES IN A PEDIATRIC HEART TRANSPLANT
(P402) Desensitization of HLA antibodies in a pediatric heart transplant
Location: Platinum Ballroom
Poster Presenter(s)
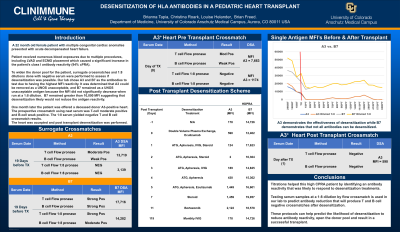
Body: A 22-month-old female patient with multiple congenital cardiac anomalies presented with acute decompensated heart failure. Her initial cPRA was 6% with class I reactivity only. Over 3 months she received numerous blood exposures due to multiple procedures, including LVAD and ECMO placement, which caused an increase in her class I antibody reactivities and her cPRA to rise to 94%. Due to this increase, surrogate crossmatches were performed to determine the strength of recipient antibodies using known HLA typed donors. Antibody reactivity to A3 and B7 were the strongest and listed as UNOS unacceptables. In the hopes of increasing the donor pool, our laboratory attempted to desensitize A3 and/or B7. Her recent serum sample was diluted 1:8 in normal serum and was tested against an A3-positive surrogate donor and a B7-positive surrogate donor. The diluted serum resulted in a negative XM against A3, but the crossmatch against B7 remained strong positive. A3 was removed from the UNOS unacceptables and one month later (1 year following initial cPRA), the patient was offered a deceased donor A3-positive heart. The prospective crossmatch using neat serum was T-cell moderate positive and B-cell weak positive with DSA detected to A3 (MFI=7,663). The 1:8 serum yielded negative T and B cell crossmatch results. The heart was accepted, and a retrospective crossmatch performed with a new serum sample on the day of surgery following intraoperative desensitization. The crossmatch results were T and B cell negative and the HDPRA showed A3 reactivity had been reduced to MFI=590. Antibody reactivity to B7 remained high (MFI=12,402) but was not DSA. Desensitization continues after transplantation (Table 1), the patient is 4-month post-transplant, and the heart continues to function well.
Conclusion: Titration of serum samples from high CPRA patients can identify antibody reactivities that will respond to desensitization treatments. Testing serum samples at a 1:8 dilution by flow crossmatch is a useful tool in predicting T and B cell negative crossmatches after desensitization. These protocols can help predict the likelihood of desensitization to reduce antibody reactivity and result in a successful transplant.
Conclusion: Titration of serum samples from high CPRA patients can identify antibody reactivities that will respond to desensitization treatments. Testing serum samples at a 1:8 dilution by flow crossmatch is a useful tool in predicting T and B cell negative crossmatches after desensitization. These protocols can help predict the likelihood of desensitization to reduce antibody reactivity and result in a successful transplant.

