Improving Time Management in Chimerism Testing: Implementing an Automated Patient Worklist
(P802) Improving time management in chimerism testing
Location: Platinum Ballroom
Poster Presenter(s)
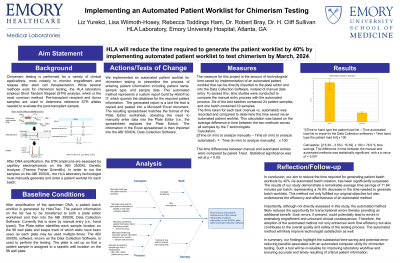
Aim: Chimerism testing is performed to monitor engraftment and relapse after stem cell transplantation. Our laboratory employs Short Tandem Repeat (STR) analysis method for chimerism assessment. After PCR amplification, the technologist must manually transfer the patient worklist from HistoTrac IT, the HLA laboratory information system, to the capillary electrophoresis instrument, a step that is lengthy and prone to human error. The aim of this quality project was to reduce the time required to generate the patient worklist by automating the process.
Method: STR analysis is performed using the GlobalFiler Kit (Applied Biosystem’s) and the samples are loaded on the capillary electrophoresis instrument (ABI 3500XL). Analysis is performed using the Chimermarker Software (Soft Genetics). To semi-automate patient worklist transfer, we developed a report generator in HistoTrac IT, which queries the database for the required patient information. The generated report is a text file that is copied and pasted into a Microsoft Excel document. The information in the Excel spreadsheet is then imported into the ABI 3500XL Data Collection Software. The time differences between the manual and automated entries were compared by paired T-test.
Results: Seven histocompatibility technologists generated the patient worklist for one batch each, using the manual and the semi-automated method. Six batches contained 24 patient samples while one batch contained 19 samples. Employing the manual method, the average time to complete the worklist was 15.39 minutes (range: 11 – 18.93 minutes, SD 2.73). The semi-automated took an average of 3.55 minutes (range: 2.91 – 4.03 minutes, SD 0.43)). The time difference between the manual and semi-automated method was statistically significant (p < 0.001). The semi-automated method resulted in an average time savings of 11.84 minutes, marking a substantial 76.9% reduction in the time needed to generate the patient worklist.
Conclusion: In summary, the findings of this study highlight the substantial time-saving and potential error-reducing benefits associated with the semi-automated, which also resulted in less time variability across technologists and batches, indicating greater reproducibility. Though relatively simple implement, this method has proven to be a valuable tool for streamlining laboratory workflow and ensuring operational efficiency and timely patient care.
Method: STR analysis is performed using the GlobalFiler Kit (Applied Biosystem’s) and the samples are loaded on the capillary electrophoresis instrument (ABI 3500XL). Analysis is performed using the Chimermarker Software (Soft Genetics). To semi-automate patient worklist transfer, we developed a report generator in HistoTrac IT, which queries the database for the required patient information. The generated report is a text file that is copied and pasted into a Microsoft Excel document. The information in the Excel spreadsheet is then imported into the ABI 3500XL Data Collection Software. The time differences between the manual and automated entries were compared by paired T-test.
Results: Seven histocompatibility technologists generated the patient worklist for one batch each, using the manual and the semi-automated method. Six batches contained 24 patient samples while one batch contained 19 samples. Employing the manual method, the average time to complete the worklist was 15.39 minutes (range: 11 – 18.93 minutes, SD 2.73). The semi-automated took an average of 3.55 minutes (range: 2.91 – 4.03 minutes, SD 0.43)). The time difference between the manual and semi-automated method was statistically significant (p < 0.001). The semi-automated method resulted in an average time savings of 11.84 minutes, marking a substantial 76.9% reduction in the time needed to generate the patient worklist.
Conclusion: In summary, the findings of this study highlight the substantial time-saving and potential error-reducing benefits associated with the semi-automated, which also resulted in less time variability across technologists and batches, indicating greater reproducibility. Though relatively simple implement, this method has proven to be a valuable tool for streamlining laboratory workflow and ensuring operational efficiency and timely patient care.

