Overcoming an Obstacle-Flow DSA XM for HIV+ Transplant Recipients
(P611) Overcoming an obstacle-flow DSA XM for HIV+ transplant recipients
Location: Platinum Ballroom
- SL
Poster Presenter(s)
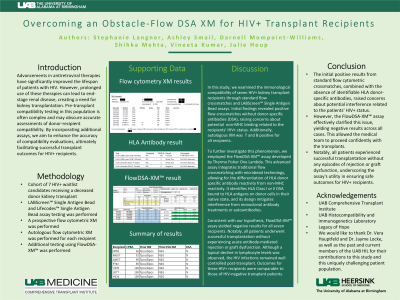
Aim: Increasingly, patients with HIV infections are living longer due to advances in anti-retroviral therapies. However, these therapies taken over long periods can contribute to end stage renal disease necessitating the need for a kidney transplant. The pre-transplant testing for these patients is often complicated and can obscure an accurate assessment of compatibility between recipient and donor. Using additional assays, we have demonstrated the ability to overcome these complications for a more accurate assessment facilitating successful transplants in HIV+ recipients.
Method: We present a series of seven HIV+ recipients who were transplanted at our center. LABScreen™ Single Antigen and LABScreen™ Mixed bead assay testing was performed for all seven recipients. A prospective Flow cytometric XM with pronased donor cells was performed as is standard protocol for deceased donor kidney offers. Additional testing using FlowDSA-XM™ was performed.
Results: Table 1 summarizes results of histocompatibility testing for the seven HIV+ patients transplanted at our center.
Conclusion: Results of standard flow cytometric XM were positive but no clear HLA donor-specific antibody was identified. We suspected that the patients’ HIV+ status was causing interference and obscuring an accurate result. The FlowDSA-XM™ assay produced a negative result in all seven cases allowing the surgical team to proceed with transplant. All patients were successfully transplanted with no rejection or graft dysfunction.
Method: We present a series of seven HIV+ recipients who were transplanted at our center. LABScreen™ Single Antigen and LABScreen™ Mixed bead assay testing was performed for all seven recipients. A prospective Flow cytometric XM with pronased donor cells was performed as is standard protocol for deceased donor kidney offers. Additional testing using FlowDSA-XM™ was performed.
Results: Table 1 summarizes results of histocompatibility testing for the seven HIV+ patients transplanted at our center.
Conclusion: Results of standard flow cytometric XM were positive but no clear HLA donor-specific antibody was identified. We suspected that the patients’ HIV+ status was causing interference and obscuring an accurate result. The FlowDSA-XM™ assay produced a negative result in all seven cases allowing the surgical team to proceed with transplant. All patients were successfully transplanted with no rejection or graft dysfunction.
